| CAS
NO. |
87-39-8 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
201-741-4 |
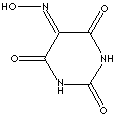
| FORMULA |
C4H3N3O4 |
| MOL
WT. |
157.09 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2933.52 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral rat LD50: >5000
mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Isonitrosobarbituric acid;
|
| Alloxan, 5-oxime;
2,4,5,6(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinetetrone,
5-Oxime; 5-Hydroxyiminobarbituric acid; 5-Isonitrosobarbituric acid; |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to pale yellow crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
240 - 250 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
Barbituric acid, chemically 2,4,6-trioxohexahydropyrimidine, a cyclic amide used as the parent compound
to produce barbiturates that act as central nervous system depressants.
Barbituric acid itself does not give sedative and hypnotic effects but the
substituted derivatives with alkyl or aryl group at position 5 provide effects.
Thiobarbituric acid, replaced oxygen atom of the urea component by sulfur, the
parent compound of the thiobarbiturates which resembles the barbiturates in its
effects. Barbiturates are drugs that acts as sedative-hypnotic agents. The
short-acting barbiturates such as thiopental are used as intravenous
anesthetics. The long-acting barbiturate such as phenobarbital is an
anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy. They are used for the
suppression of anxiety, the induction of sleep, and the control of seizures.
Commercially available barbiturates are;
- Amobarbital
- Aprobarbital
- Butabarbital
- Butalbital
- Hexobarbital
- Mephobarbital
- Pentobarbital
- Phenobarbital
- Secobarbital
- Talbutal
- Thiobarbital
- Thiopental
Alternative medications, namely
benzodiazepines have replaced for barbiturates due to a high potential for
abuse.
Violuric acid,
isonitroso-
functional group substituted barbituric acid,
is used
in biological
research. Violuric acid
is active as an antihypoxic agent.
Violuric acid
is the oxime form of alloxan
which produces selective destruction of the beta
cells of the pancreas.
|
Product
|
CAS
RN.
|
| Alloxan |
50-71-5 |
| Alloxantin |
76-24-4 |
| Violuric acid |
87-39-8 |
| Alloxanic acid |
470-44-0 |
| Violuric acid
monosodium salt
|
825-29-6
|
| Alloxan
monohydrate |
2244-11-3 |
| Oxypurinol |
2465-59-0 |
| 1,3-Dimethylalloxan |
2757-85-9 |
| 2,4,5,6(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinetetrone hydrate |
3237-50-1 |
| Alloxanthin |
28380-31-6 |
|
5-((4-Methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)hydrazone) alloxan |
31353-87-4 |
| 1-Phenylvioluric acid |
82628-28-2 |
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to pale yellow crystalline powder |
|
IDENTITY
(IR)
|
pass
|
|
PURITY
(G.C.)
|
99.0%
min
|
|
MELTING
POINT
|
240
- 250 C
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/38-43, Safety
Phrases: 22-26-28 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF NITROSO-
|
| Nitroso is the
prefix for NO- radical with
trivalent nitrogen also known as hydroximino; oximido. Substances in which this
group is attached to an oxygen atom are called nitrites (esters of nitrous
acid); those in which the nitroso group is attached to a metal ion are called
nitrosyls. Nitroso (-N=O) groups and azo (-N=N-) groups impart colour to the
compound as these groups absorb light of characteristic wavelengths.
|
